Our funding comes from our readers, and we may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
The Best Free Open Source NetFlow Analyzers for Windows and Linux/Unix

UPDATED: January 29, 2024
Looking for a Free Open Source NetFlow Analyzer for Windows, Linux, or Unix? Look no further, we've compiled the ultimate list of Open Source tools to help with your network monitoring tasks.
As many of you already know, NetFlow is a protocol/standard developed by Cisco for collecting/transferring/analyzing network data using software packages to get a better understanding of what is happening on your network, along with further analysis of bandwidth usage, etc.
Netflow allows administrators to take the processing of network data away from switches and routers and send the flow packets and information to a collector that further analyzes that data to free up resources on the network device itself.
Here is our list of the best free NetFlow analyzers and collectors for Windows and Linux:
- NTop – EDITOR’S CHOICE Famed for its key product, called ntopng (Next Generation), this open-source project has produced a list of free tools that are all centered on traffic analysis. This toolset uses an impressive range of networking protocols to extract traffic data and device status information. Runs on Linux, Unix, macOS, and Windows.
- Flow-tools A package of tools to collect NetFlow data and generate analysis reports. Runs on Linux.
- FlowScan This neat package analyzes NetFlow data collected by other tools, such as Flow-tools or cflowd. Runs on Linux and Unix.
- EHNT Extreme Happy Netflow Tools is a free interpreter for NetFlow data but can’t go past NetFlow version 5. Runs on Linux and Unix.
- BPFT Berkeley Packet Filter Traffic uses libpcap procedures to capture traffic packets. Runs on Unix.
- cflowd A much-liked free NetFlow data extraction tool that has gone out of production so you should use Flow-tools instead. Runs on Linux.
- Panoptis A DDoS blocker that collects and analyzes NetFlow data, looking for indicators of attack. No longer maintained but still works and runs on Linux.
- Pmgraph A network traffic graphing tool that extracts flow information from a network through NetFlow and sFlow. Runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, or Unix.
- InMon sFlow Toolkit This sFlow analyzer relies on other systems for data collection and can also work with NetFlow data. Runs on Windows and Linux.
- NDSAD Traffic Collector This service only works with NetFlow v5 but it will interpret data to show network activity. Runs on Windows, Linux, and Unix.
- NFsen/NFDump Netflow Sensor interprets data collected by NFDump to create graphical displays of traffic flows. Runs on Linux, Unix, and macOS.
There are many commercial Netflow (or sflow, jflow, rflow, cflow, or netstream) that are Available for Free Download and use that we've recently detailed in this post that are also free of charge too.
These Software packages are great if you are just getting into network analysis using Netflow, as they are designed to be very user-friendly and can be set up in relatively little time.
Check them out HERE if you want to see what they're all about.
On the other hand, if you are looking for an Open-Source alternative, you're in luck. We've put together a large list of Free Open Source Netflow Analyzers/Collectors to help you collect, analyze and scrutinize traffic and bandwidth to help you keep track of what's going on in your network.
Using an open-source network analyzer/collector allows you the flexibility of customizing the software packages and reports as you wish if necessary.
These software packages can be used on a wide variety of operating systems including Windows and Linux/Unix.
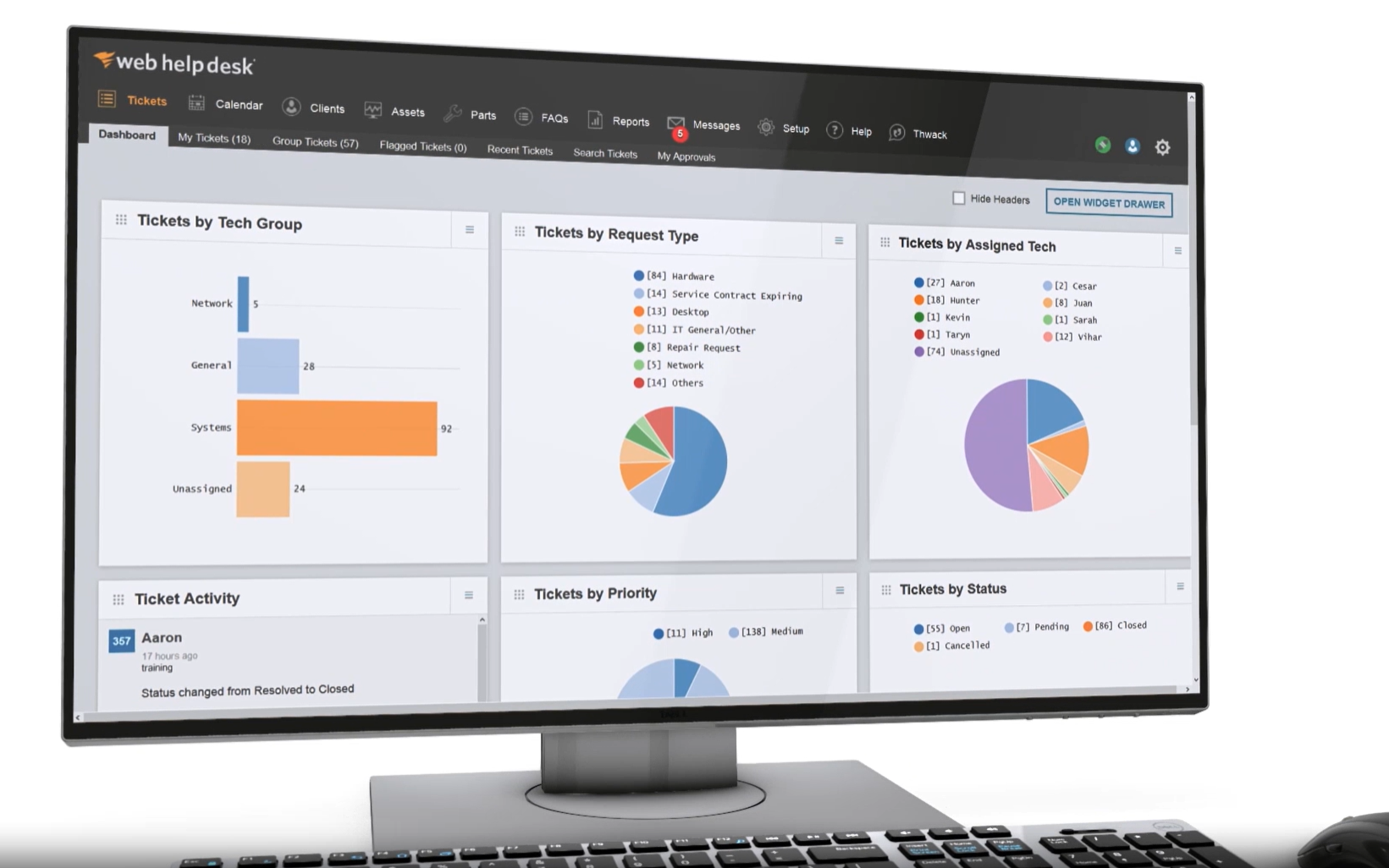
The Best Open Source Netflow Tools/Analyzers
1. NTop (or Ntopng)
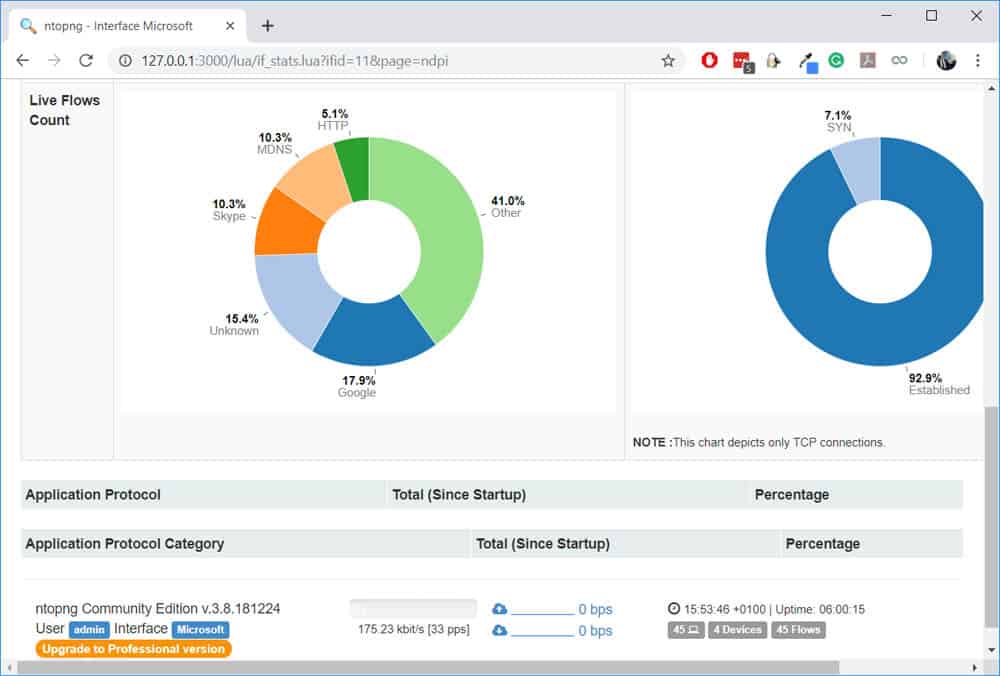
Probably the most well-known open source traffic analyzers, Ntop, is a web-based tool that runs on Ubuntu x64 versions, CentOS/Redhat x64 Linux flavors, Windows x64 Operating systems, BeagleBoard ARM, Ubiquity networks EdgeRouter and even Mac OSX per their github site. NTopng also includes support for sFlow and IPFIX (through nProbe add-on), as its becoming a new standard that many manufacturers are using for flow analysis. RRD is used for databases and storing data on a per-host level.
Key Features:
- Traffic extracts: Packet capture
- Flow protocols: NetFlow, sFlow, J-Flow, NetStream, and IPFIX
- Security scanning: Deep packet inspection
- Active protection: Intrusion prevention system
- Performance improvements: Traffic shaping
Unique Feature
NTop is a pretty unique tool among other open-source Netflow analyzers. It can collect data from a wide range of networking protocols, which makes it more than just a data collector, but also a robust network monitor. Plus, ntopng comes with distinctive features such as geolocation, app recognition, and web-based graphs.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend NTop, especially its Next Generation version (nTopng) for its extensive protocol support on traffic data extraction and device status information (via graphical representation). Additionally, this network monitoring tool is pretty versatile; It runs on a variety of platforms (Linux, Unix, macOS, and Windows). It's also pretty powerful, thanks to its ability to utilize sFlow and IPFIX.
Who is it recommended for?
NTop is recommended for network admins and IT pros looking for a robust NetFlow analyzer with powerful traffic analysis capabilities. It's also perfect for people using firewalls like pfSense who need a way to visualize and track bandwidth usage.
Pros:
- Reliable system: A long-running tool that is thoroughly tested
- Expandable: Extended capabilities through plug-ins
- Subscription options: Free and paid editions
- Multiple operating systems: Available for Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Traffic volume investigation: Provides protocol analysis
Cons:
- Free tool limitations: Functionality extension plug-ins are only available with the paid editions
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Ntop is our first choice for a free NetFlow analyzer and collector because of the project’s star product ntopng. This widely-used workhorse has been around for a long time, so its extensive use has allowed all the major defects in the code to be spotted and fixed. This service will run on any operating system and also on Docker. Its use of a very long list of network protocols to extract network data makes it more than just a collector, it can fulfill the functions of a free network monitor.
Download: https://www.ntop.org/
Official Site: https://www.ntop.org/get-started/download/
OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, macOS
2. Flow-tools
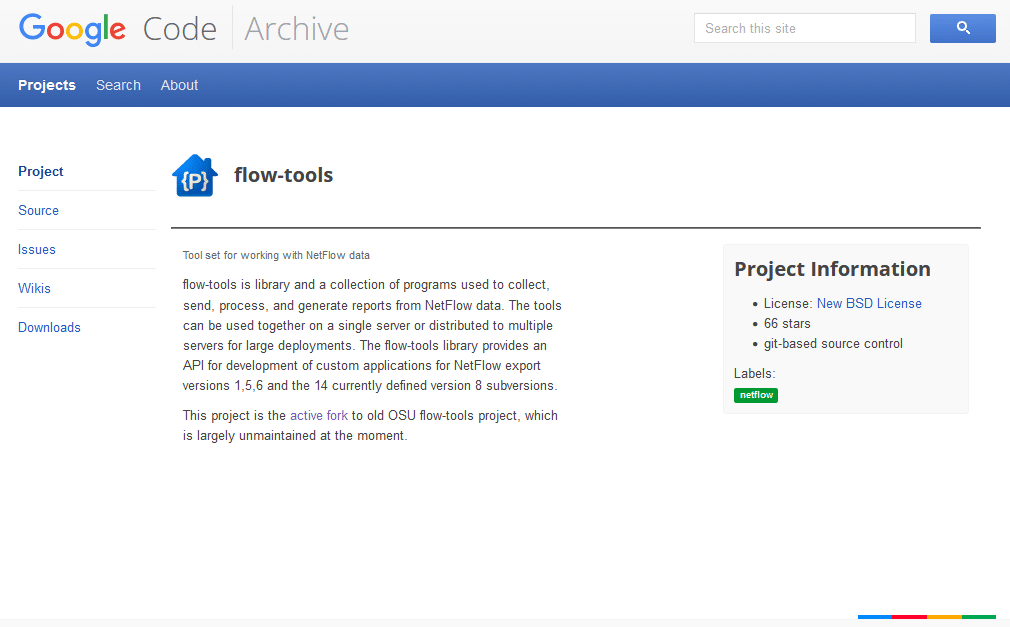
Flow-tools is a toolset that can be used to Collect, Send, Process and generate Reports for Netflow data flows and provides an API for developing custom features and applications. Flow Tools is hosted at http://flow-tools.googlecode.com.
Key Features:
- No charge: Free tool
- Data from switches: Collects and processes NetFlow
- Produces reports: Initial analysis
- Adaptable: The source code is available
Unique Feature
One distinctive feature of Flow-tools is its modular architecture, which allows you to add a vast number of add-ons. It also supports many different versions of NetFlow (1, 5, 6, and 8), so you can use it in a variety of network environments.
Why do we recommend it?
Flow-tools is recommended for its wide range of features, so it would handle just about anything you throw at it. Flow-tools is really versatile when it comes to handling NetFlow data flows. If you're looking for a robust NetFlow data handling tool, Flow-tools is definitely worth checking out.
Who is it recommended for?
Flow-tools is ideal for network administrators and analysts, especially those who manage large networks. It is a perfect tool for anyone who needs to collect, process, and generate reports from NetFlow data.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Flow-tools.
Pros:
- Open source: You can read the program code and change it if you like
- Foundational program: Use it to build your own traffic analysis tool
- Command line system: No graphical user interface
- Runs on Linux and Unix: No version for Windows
Cons:
- Outdated: The latest version dates back to 2010
3. FlowScan
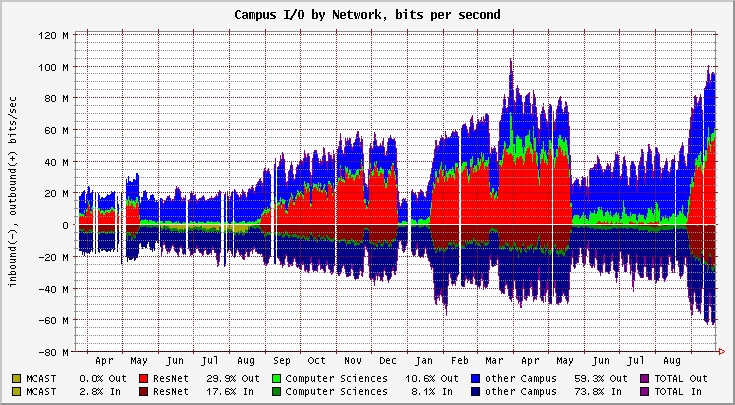
Flowscan is more of a visualization tool that analyzes and reports Netflow data and can produce visual graphs that are in “near” real-time to see whats going on in your network. Flowscan can be deployed on a GNU/Linux or BSD system and uses some of the following packages in order to correctly collect and process flows. The last major component is Flowscantool which is used to store all flow information in its database.
Key Features:
- Relies on cflowd: A widely-used NetFlow collector
- Graphical display: Creates time-series graphs
- Open source: Get the code
Unique Feature
One distinctive feature of FlowScan is its emphasis on a command-line interface. Its focus on providing detailed, text-based information sets it apart as a practical and effective NetFlow analyzer.
Why do we recommend it?
FlowScan is recommended as one of the best open-source NetFlow analyzers because, even though the interface is a bit old-fashioned, the software is simple to use. Plus, the graphical representations are clear and detailed, and the grid formats and extensive graph legends make it easy to interpret the data.
Who is it recommended for?
FlowScan is recommended for those network admins who prefer the command-line interface with a straightforward NetFlow analyzer. It is a tool that focuses on providing essential network activity insights without any bells or whistles. So, if you value functionality over aesthetic design, then FlowScan is totally recommended.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Flowscan.
Pros:
- An enthusiastic-written tool: Free to use
- Available for Linux and Unix: No Windows version
- Can run on top of flow-tools: Enhances functionality
Cons:
- Old code: Hasn’t been updated since 2014
4. EHNT
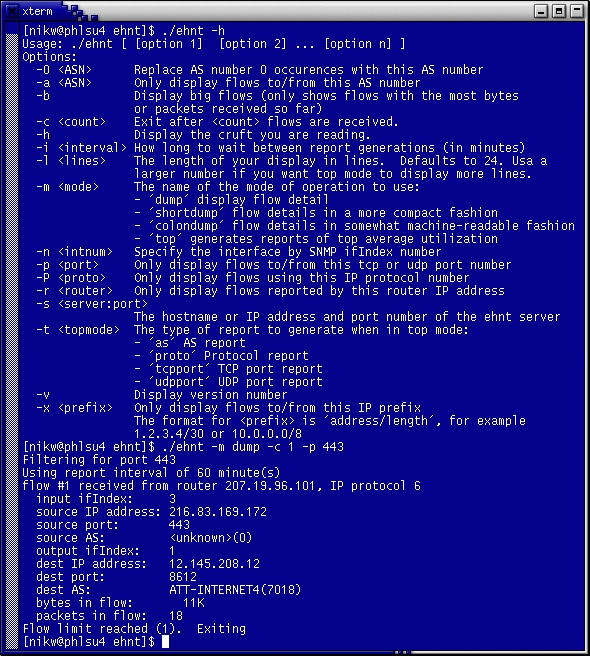
EHNT (which is pronounced “ent”) is an acronym for Extreme Happy NetFlow Tool. This is a command line tool that supports Netflow Version 5 only and provides reports for intervals between 1 min to 24 hrs and provides information about IP protocols, TCP/UDP ports, and more.
Key Features:
- Command line tool: Quick to run
- NetFlow v5: Check your version requirements
- Runs on Linux and Unix: No version for Windows
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend EHNT because it is easy to use. It comes with a straightforward terminal interface that makes it quick and easy to process NetFlow version 5 data. In addition, the results are also easy to understand and use.
Who is it recommended for?
EHNT is recommended for network administrators and analysts who prefer a simple terminal-based tool for processing the NetFlow v5 data interface. So, if you care more about getting stuff done than having a pretty interface, then EHNT is totally worth checking out.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to EHNT.
Pros:
- Program available: Source code written in Perl
- Fast output: Useful for getting a dump of NetFlow data
- Traffic examination: Protocol analysis option
Cons:
- A little outdated: Last updated in 2013
5. BPFT

BPFT (which stands for Berlekey Packet Filter Traffic collector) is built on top of the BPF (pseudo-device) and libpcap for capturing IP traffic. BPFT captures Source/Destination IPs & Ports, number of transmitted/received bytes which are all stored in one compact form binary file.
Key Features:
- BPF: Berkeley Packet Filter emulator
- Packet capture: Uses libpcap as a collector
- Reads from the host computer: Gathers traffic from a network interface
Unique Feature
The uniqueness of BPFT is that it uses Berkeley Packet Filter procedures to capture and store IP traffic information, which means it can collect a lot of detailed data.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend BPFT as one of the best open-source NetFlow analyzers because it excels in capturing and storing detailed network information in a compact binary form (using Berkeley Packet Filter procedures).
Who is it recommended for?
BPFT is an ideal tool for Unix users who need detailed information about IP traffic. It's especially recommended for network administrators who need reliable and extensive data capture.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to BPFT.
Pros:
- Doesn’t communicate with switches: Uses a computer’s network interface in promiscuous mode
- Gathers data for analysis in other tools: Save packets to file
- Stores packets: Facilitates packet analysis
Cons:
- Packet capture tool: Not a NetFlow collector
6. cflowd
cflowd is a tool that is made for analyzing Netflow-enabled devices and includes modules for collecting, storing, and analyzing Netflow data. Apparently, cflowd is no longer being supported per their website and is directing users to use flow-tools with FlowScan in order to take advantage of cflowd and its modules.
Key Features:
- Command line tool: No graphical user interface
- Multiple NetFlow versions: NetFlow v5, 8, 9, and 10
- No charge: Free to use
Unique Feature
A unique feature of Cflowd is its capability to sample all kinds of traffic flows, including IPv4, IPv6, MPLS, and Ethernet, through a router.
Why do we recommend it?
Cflowd is recommended for its traffic flow monitoring capabilities, especially for being able to analyze Flexible NetFlow (FNF) traffic data and export flow data to an IPFIX analyzer. It's really good at monitoring traffic flowing through routers, and it provides detailed insights into network activity.
Who is it recommended for?
Cflowd is an ideal open-source NetFlow analyzer for network admins and engineers. It's perfect for anyone who needs to do in-depth traffic sampling and analysis for things like capacity planning, trends analysis, workload characterization, traffic engineering, network planning, and network monitoring.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to cflowd.
Pros:
- Additional capabilities: Also compatible with IPFIX
- Highly recommended: Recommended by Cisco
- Up to date: Recently updated
Cons:
- Warning: Although switch producers recommend this tool, the organization that hosts it doesn’t
7. Panoptis
According to the SourceForge page, this project is no longer being developed or supported and was an open-source project that used NetFlow data to help detect and stop (Distributed) Denial of Service attacks. It is no longer supported or being updated, so use at your own risk. Check out their Sourceforge page for more information and a download link.
Key Features:
- Network protection: Detects and blocks DDoS attacks
- Additional usage: Gatherts NetFlow data
- Network traffic analysis: Analyzes NetFlow
Unique Feature
Panoptis' distinctive feature is its focus on using NetFlow data for DDoS attack detection and prevention.
Why do we recommend it?
Panoptis is recommended for its highly effective network security tool (N-IDS), which specializes in detecting and preventing DoS/DDoS attacks. In addition, the tool can process NetFlow data from routers, making it a valuable network security tool.
Who is it recommended for?
Panoptis is recommended for network security pros and administrators who need a tool for detecting and mitigating DoS/DDoS attacks using NetFlow data. It is recommended for advanced users familiar with C++, SNMP access, and Python.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Panoptis.
Pros:
- Goes straight to the source: Collects NetFlow data from switches
- Traffic pattern analysis: Looks for signs of traffic surges
- Automated alerts: Sends an email notification
Cons:
- Outdated code: Hasn’t been updated since 2013
8. pmgraph
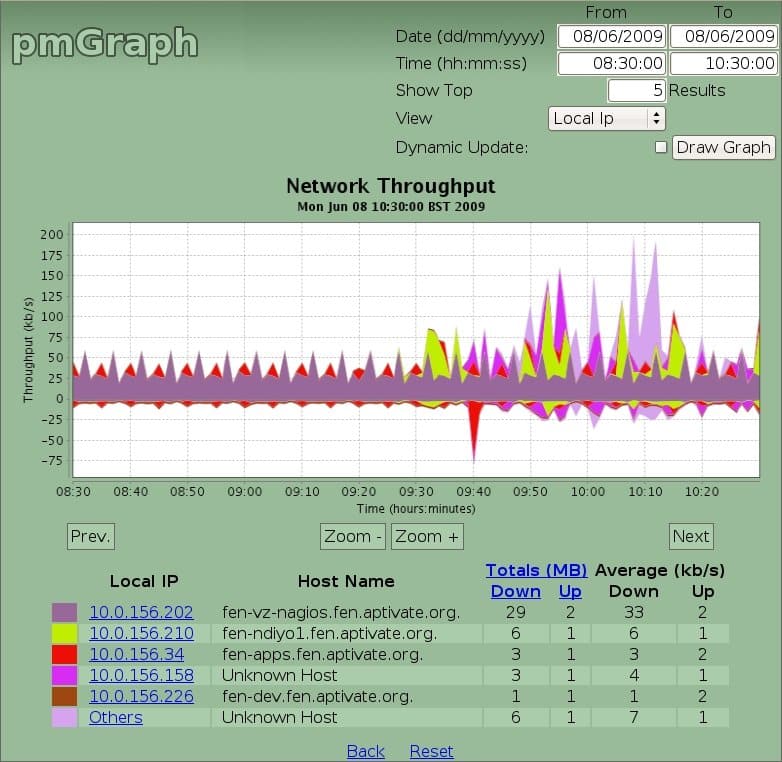
pmGraph is a great open-source tool for graphing and monitoring bandwidth using pmacct, which is a network monitoring and auditing tool. pmacct collects and monitors traffic using Netflow or Sflow on network devices (including firewalls, routers and switches) into a database and allows for analysis of that data using pmGraph. The software was developed by Aptivate staff and volunteers and looks to still be active.
Key Features:
- A graphical frontend: Requires pmacct
- Network views: Shows traffic data
- DNS checks: Host name resolution
Unique Feature
One distinctive feature of pmGraph is that it provides graphical network traffic analysis.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend pmGraph as one of the best free open-source NetFlow analyzers because it is easy to install and configure. This tool is ideal for graphing and monitoring bandwidth usage through NetFlow and sFlow. While it may have some limitations, it provides essential insights into bandwidth usage.
Who is it recommended for?
pmGraph is recommended for network and systems admins who are responsible for monitoring network traffic. It is designed to be user-friendly and to provide graphical representations of traffic flows, so it can be used by anyone, even those without technical background.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to pmGraph.
Pros:
- Visualizations: Provides graphs for data collected by pmacct
- Repeatable queries: Extracts traffic data stored in a MySQL database by pmacct
- Runs on Debian Linux: No version for Windows
Cons:
- Old code: Was written in 2006
9. InMon sFlow Toolkit
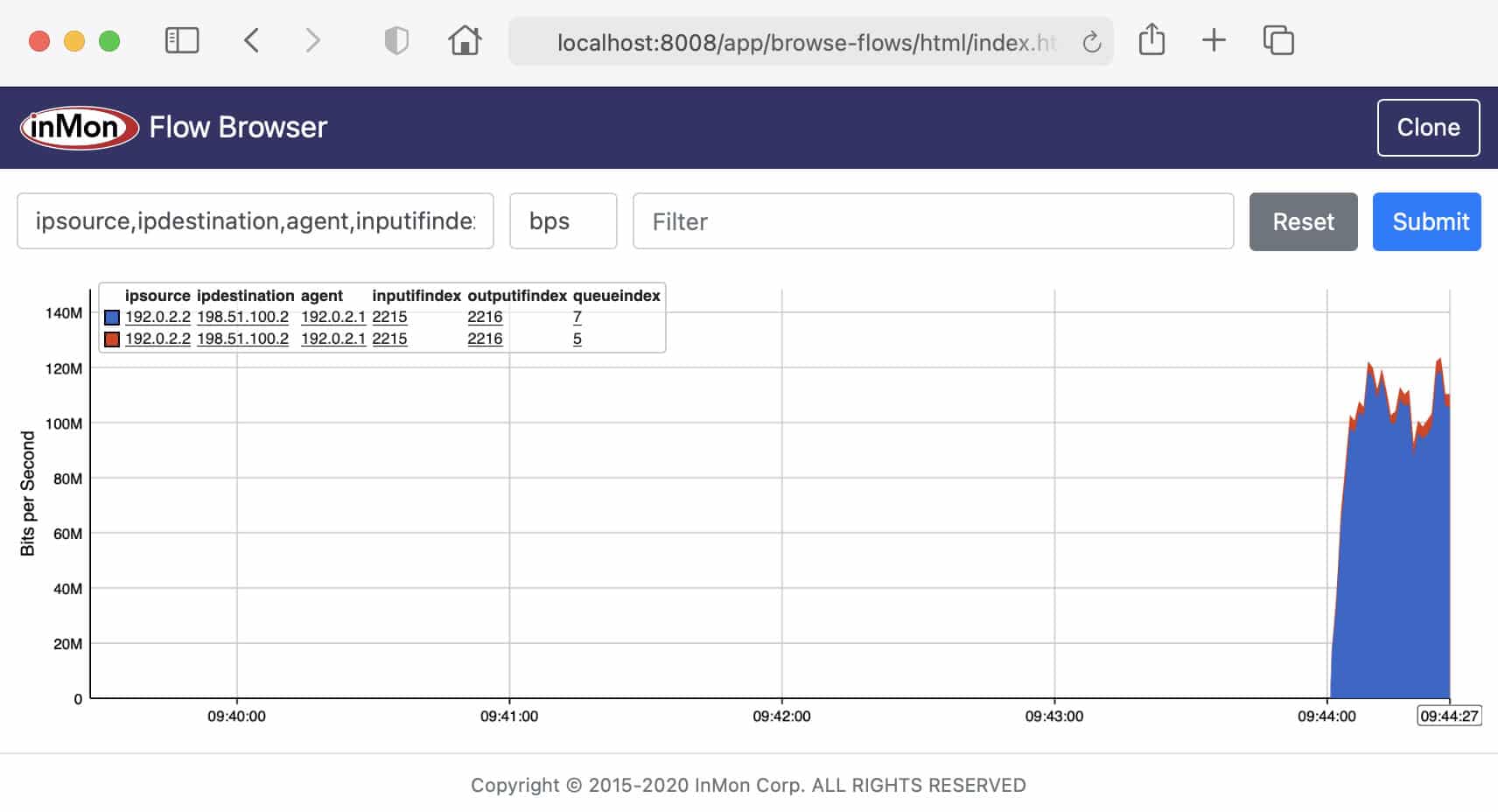
sFlow toolkit is an open-source software package the is used for analyzing sFlow data and can be used with other utilities including tcpdump, ntop and Snort for further analysis. “sflowtool” is the main component of the sFlow toolkit software and is a command-line utility that gives you the ability to view network traffic devices in real-time. It interfaces with other software packages for mapping out graphical images of IP flow. sflowtool is also available for Windows as well per their website.
Key Features:
- From the creators of sFlow: The definitive sFlow collector
- Substitutes for NetFlow: Derived from NetFlow
- No charge: Free command line tool
Why do we recommend it?
If you are looking for an alternative to Cisco’s NetFlow, then we recommend checking out InMon’s sFlow. The InMon sFlow Toolkit can be used in conjunction with other utilities like tcpdump, ntop, and Snort for further analysis. This toolkit is particularly valuable for businesses looking for a cost-effective solution.
Who is it recommended for?
The InMon sFlow Toolkit is recommended for small businesses and organizations looking for improved network monitoring technology that NetFlow can’t provide. sFlow is more scalable, real-time, and gives you more detail in its reports. This tool is ideal for Network Operations Center (NOC) environments.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to sFlow Toolkit.
Pros:
- Authoritative source: This is the original and definitive program for collecting sFlow
- Free frontend available: Has a graphical display counterpart, called sFlow Trend
- Data collector for analyzers: Can forward sFlow data to other applications for analysis
Cons:
- Limited functionality: Good for collecting traffic data but not for analysis
10. NDSAD Traffic Collector
NDSAD, which stands for NetUP's Data Stream Accounting Daemon, was developed by NetUP as a tool to capture packets and generate Netflow v5 data streams and was specifically used for ISP billing purposes. The software still seems to be supported as well.
Key Features:
- Multiple OSs: For Linux or Windows
- Packet capture: Collects packets with libpcap or WinPcap
- Doesn’t generate network traffic: Listens on the host’s network adapter
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend NDSAD Traffic Collector because it can translate captured traffic data into the NetFlow v.5 format. This is a really important feature for network administrators and security professionals who need to collect statistics on network traffic for things like security monitoring or usage-based billing.
Who is it recommended for?
The NDSAD Traffic Collector is recommended for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and ISPs that require a tool for generating NetFlow v5 data streams. It is particularly useful for billing and accounting purposes.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to NDSAD Traffic Collector.
Pros:
- Packet sniffer: Gathers packet data from the network
- Passive operations: Relies on the switch outputting NetFlow data onto the network
- Originally used for video traffic: Designed for IPTV boxes
Cons:
- Dated program: Hasn’t been updated since 2016
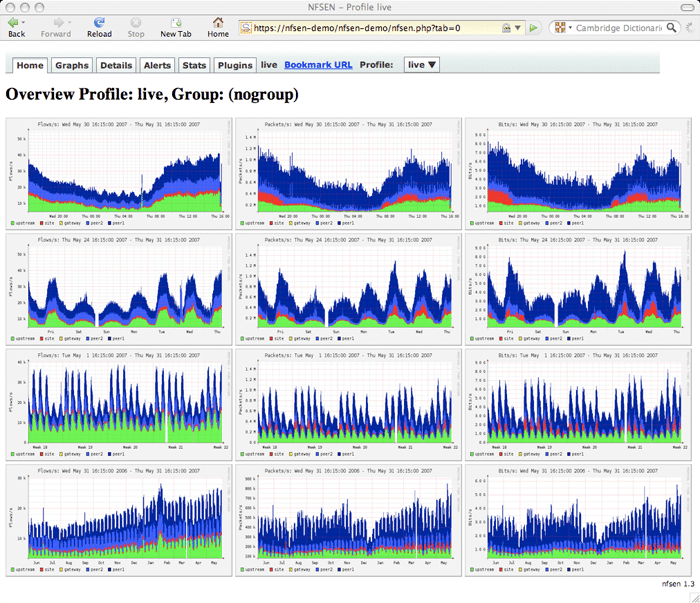
11. NFsen/NFDump
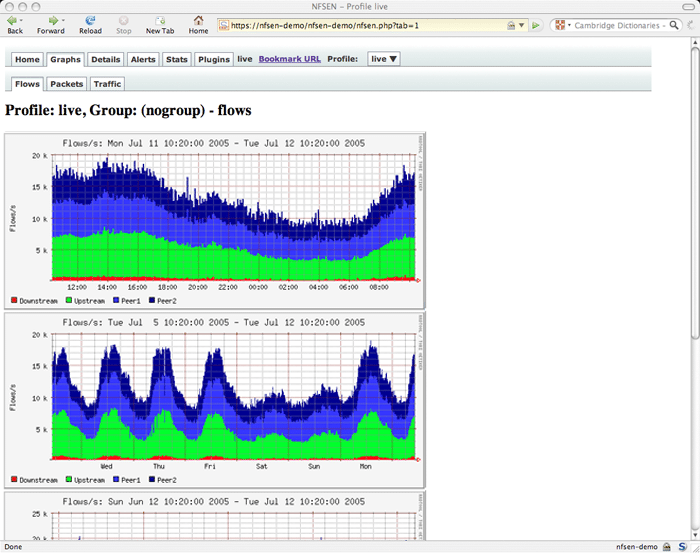
NFsen, which is short for Netflow Sensor, is a web-based front-end tool for nfdump to present the user a nice graphical image of all the data nfdump pumps out. You have the ability to generate reports of your netflow data with information including Flows, Packets and bytes using RRD database tool, as well as setup alerts and view historical data. The nfsen project is still very active and can be downloaded from its Sourceforge page here and runs on any Unix/Linux systems. You'll need PHP, PERL (along with Perl Mail::Header and Mail::Internet modules), RRD Tools module and Nfdump tools installed on your system in order to use it correctly.
Key Features:
- Visual display: NetFlow traffic graphs
- Shows data as it arrives: Live traffic graph
- Stores data for later use: Historical analysis
Why do we recommend it?
NfSen is recommended because it is a comprehensive, user-friendly netflow analyzer with advanced features like alerts and custom plugins. NFsen/NFDump also integrates with nfdump tools for command-line and graphical visualization.
Who is it recommended for?
NfSen is a versatile Netflow analyzer for Windows, Linux, and Unix. It's recommended for network admins, security pros, and anyone who needs to monitor network traffic. This tool is suitable for small business network or a large enterprise infrastructure
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to NfSen.
Pros:
- Collects and interprets data: Gathers NetFlow data and displays a time-series graph
- Writes to file: Stores NetFlow data for historical analysis
- NetFlow forwarder: Can prepare data for use in other analytical tools
Cons:
- Outdated code: Last updated in 2011
If you are not convinced that you've found any Open Source Netflow Analyzers that will suit your needs, due to either your skill level or understanding of Unix/Linux systems. You can always try one of these Free netflow software packages that we've recently reviewed that will work for Windows systems.
Most, if not all those downloads are free and can be set up and used very quickly – some of them also offer pro versions of the software that can be had for very little investment. Check them out and let us know what you think.