Our funding comes from our readers, and we may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
The Best Open Source Router OS Software for Small or Large Networks

UPDATED: February 26, 2024
Get the best OS for your router; totally free and community supported.
Routers have traditionally been created using proprietary software, which means the source code is closed and cannot be modified by users. However, open-source router operating systems have grown in popularity in recent years, providing customers with additional freedom, customization, and control over their networks.
Here is our list of the best Open Source Router OS Software for Small or Large Networks:
- OpenWrt A Linux-based open-source router firmware that can be installed on a wide range of hardware platforms. It provides a customizable, modular, and lightweight platform for creating routers, gateways, and other network devices.
- pfSense An open-source firewall and router platform based on FreeBSD. It provides a wide range of features, including VPN, load balancing, traffic shaping, and more. pfSense can be used to build a range of network devices, from small home routers to large enterprise firewalls.
- DD-WRT Another open-source router firmware based on Linux. It provides advanced features like VPN, VLAN, and QoS, and it can be installed on a wide range of routers. DD-WRT is suitable for both home and enterprise use.
- VyOS Based on Debian Linux. It provides a wide range of routing and security features, including VPN, firewall, NAT, and more. VyOS can be used to build a range of network devices, from small home routers to large enterprise firewalls.
- RouterOS Developed by MikroTik. It provides a wide range of features, including VPN, firewall, hotspot, and more. RouterOS can be used to build a range of network devices, from small home routers to large enterprise firewalls.
- Tomato An open-source router firmware based on Linux. It provides advanced features like VPN, QoS, and traffic monitoring, and it can be installed on a wide range of routers. Tomato is suitable for both home and enterprise use.
The flexibility to tweak and personalize the software to meet the specific needs of a given network is one of the key benefits of utilizing an open-source router OS. This is especially crucial for corporations and organizations with distinct needs or applications. Users of open-source software can alter the code to add new features, improve performance, or increase security.
Another advantage of open-source router operating systems is their transparency. Users are frequently left in the dark about how the router works and what data it may be gathering when using proprietary software. Nevertheless, with open-source software, the source code is openly available, allowing customers to understand exactly how the router works and have more control over how their data is handled.
There are several variables to consider when choosing an open-source router OS. The amount of support and community participation surrounding the product is one of the most significant. A strong user and developer community can assist ensure that the program is always up-to-date and safe, as well as provide essential resources for troubleshooting and modification.
Another crucial element is the range of features and functionalities given by the software. Certain open-source router operating systems may include more advanced routing and security capabilities, whereas others may be more focused on usability and flexibility. When choosing a router OS, it is critical to analyze the specific needs of a given network and to select one that delivers the correct combination of features and functionality.
The Best Open Source Router OS Software for Small or Large Networks
Our methodology for selecting Open Source Router OS Software for Small or Large Networks
With our proven expertise and experience, we have found the below methodology useful for selecting the best open-source router OS. Go through the list below.
- Clearly outline your specific needs, such as performance, scalability, and security features.
- Conduct thorough research on available open-source router operating systems.
- Look for features like VPN support, firewall capabilities, QoS, VLAN support, and easy configuration.
- Evaluate factors like throughput, latency, and stability under load.
- Check for hardware compatibility supported by the router OS.
- Consider security features and in-built security mechanisms.
- Evaluate factors like the release cycle, ongoing development activity, and the commitment of the community to maintaining the project.
- Consider associated costs such as hardware requirements and support contracts for commercial hardware.
1. OpenWrt
OpenWrt is a popular open-source router firmware that has been around since 2004. It offers a range of features and functions that make it a viable option for both small and large networks. One of the most notable features of OpenWrt is its customizability. Users can choose from a wide range of packages and modules to install on their routers, allowing them to tailor their devices to their specific needs. This can be particularly useful for those who need advanced features like VPN, QoS, and more.
Key Features:
- Frequently Updated: OpenWrt is constantly updated with the latest security patches, bug fixes, and necessary feature additions to keep the system secure, stable, and equipped with cutting-edge networking technologies.
- Firewall Functions: With customizable rules and policies, users can protect their network from unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and unwanted traffic, ensuring a secure and safe networking environment.
- IPv6 Enabled: This enables seamless integration with IPv6 networks and ensures compatibility with modern networking standards.
- Traffic Shaping Possible: By controlling bandwidth allocation and managing network congestion, traffic shaping ensures optimal performance for critical applications and services.
Why do we recommend it?
OpenWrt is recommended because it offers a flexible approach to firmware. Unlike fixed options, it lets you change and add software easily, tailoring your device to fit any purpose. This means freedom from pre-set configurations, empowering users to customize their network exactly how they want. It's all about flexibility and control.
Another benefit of OpenWrt is its lightweight design. The firmware is optimized for performance and can run on a range of hardware platforms, including routers with as little as 4MB of flash storage. This makes it an ideal choice for those who want to repurpose an older router or use a low-cost device. OpenWrt is also known for its security features. It provides regular updates to address security vulnerabilities and includes features like packet filtering, NAT, and VPN to help keep networks secure.
Who is it recommended for?
OpenWrt is great for developers who want to create applications without starting from scratch and for users who wish to personalize their devices in unique ways. It's beneficial for those who need advanced networking setups like Quality of Service, NAT, or VLAN tagging. It's a versatile tool for both developers and tech-savvy users.
Pros:
- Limitless Customization: With OpenWRT, you can customize your router and make it do exactly what you want.
- Enhanced Security: You get regular updates and lots of help from a big community, which keeps your router safe from online breaches.
- Performance Boost: You can make your network faster and smoother for things like gaming or watching videos without any interruptions.
- It’s Free!: You don't have to pay a single penny to use OpenWRT.
Cons:
- Device Compatibility: some users find compatibility issues in devices because of individual router functionality.
As open-source software, OpenWrt is free to use and distribute. However, some hardware manufacturers offer pre-installed versions of the firmware for a fee. One potential downside to OpenWrt is the lack of official support. While there is an active community of developers and users who provide support and guidance, there is no official customer support team. This can be a concern for those who require assistance with their router.
Ultimately, OpenWrt is a powerful and versatile open-source router firmware that offers a range of features and functions. Its customizability, lightweight design, and security features make it a popular choice for both small and large networks. However, users should be aware of the potential downsides, including the need for technical expertise and the lack of official support.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
OpenWrt stands out as a top choice because it has crucial features like firewalls, protection from cyber threats, and VPN support, safeguarding your network against attacks. Regular updates keep security tight, shielding users with the latest defenses. Furthermore, OpenWrt is designed to be simple to use, making it suitable for a wide spectrum of users, from beginners to specialists. With its combination of security, usability, and continuous improvement, OpenWrt shines as the premium choice for router operating systems.
OS: Linux OS
2. pfSense
pfSense is a FreeBSD-based open-source firewall and router platform. It has a wide range of features and functionalities, making it a popular choice for both small and big networks. The versatility of pfSense is one of its most prominent advantages. It may be used to build everything from small home routers to massive enterprise firewalls.
Key Features:
- Stateful Packet Inspection: This ensures that only legitimate traffic conforming to established connection states is allowed through the firewall.
- IP/DNS-Based Filtering: This feature allows administrators to enforce network policies, block unwanted traffic, and restrict access to certain websites or services.
- Anti-Spoofing: By verifying the source address of incoming packets against the network topology, pfSense protects against IP spoofing attacks, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of network traffic.
- Time-Based Rules: This feature enables the implementation of time-based access controls, scheduling of network activities, and enforcement of policies during designated periods, enhancing security and efficiency in network management.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend pfSense for its robust network security solutions, ideal for enterprises, large businesses, and small offices/home offices (SOHO). Powered by pfSense Plus software, Netgate's offerings combine cutting-edge technology to simplify network protection. Built on dependable platforms, they ensure top-notch performance, stability, and trustworthiness. With pfSense, safeguarding your network becomes more manageable, providing confidence in your security measures.
One of pfSense's most notable features is its robust firewall capabilities. It provides capabilities such as sophisticated packet filtering, stateful inspection, and intrusion detection and prevention to help keep networks secure. Moreover, pfSense supports VPN, load balancing, traffic shaping, and other network functions, making it a complete network solution.
pfSense is also noted for its ease of use. Its web-based interface is intuitive and user-friendly, making it easy to configure and manage even for those who are not networking specialists. Furthermore, pfSense releases regular updates to correct security flaws and improve efficiency. pfSense is free to use and share as open-source software. Commercial support and services are, however, available for individuals who require further assistance or features.
One disadvantage of pfSense is that it requires more powerful hardware than some other router software solutions, which may restrict its usefulness for some users. Another potential disadvantage is that pfSense may be more difficult to install and configure than other router software solutions. While the web-based interface is simple to use, users may need to spend more time configuring the product to match their individual requirements.
Who is it recommended for?
pfSense is recommended for network administrators and IT professionals seeking robust firewall capabilities. Experts in cybersecurity utilize pfSense for its advanced features like stateful packet inspection and intrusion prevention, enabling it to block unwanted traffic effectively and defend against malicious attacks on networks.
Pros:
- Filtering and NAT Forwarding: pfSense allows you to control and filter network traffic, deciding what can enter or leave your network. NAT (Network Address Translation) forwarding helps manage connections between different networks.
- Routing: pfSense provides robust routing capabilities, allowing you to manage traffic between different networks or subnets efficiently.
- IDS/IPS: Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) features to enhance security by monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities and blocking potential threats in real time.
Cons:
- Sometimes Too Aggressive: IDS/IPS systems can be overly sensitive, leading to legitimate traffic being flagged as malicious. This can result in disruptions to network operations or unnecessary blockages of legitimate traffic.
pfSense is a robust and adaptable open-source router and firewall platform with several features and functionalities. Many customers like it because of its flexibility, effective firewall features, ease of use, and regular upgrades. However, before deciding to utilize pfSense, users should be aware of the potential hardware requirements and configuration complexity.
3. DD-WRT
Since 2005, DD-WRT has been a popular open-source router firmware. It has a variety of features and functionalities that make it suitable for both small and large networks. Customizability is one of DD-most WRT's most significant features. Customers can install a variety of packages and modules on their routers, allowing them to personalize their devices to their individual needs. This is especially handy for individuals that require advanced capabilities such as VPN, QoS, and others.
Key Features:
- Strong Community Support: it has a community of users and developers who provide extensive support, guidance, and resources so you can quickly get troubleshooting assistance and other help.
- Open Source/No Additional Cost: You can enjoy advanced router features and customization options without incurring additional costs, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious users and businesses.
- Extensibility: DD-WRT offers extensibility through support for add-ons, plugins, and custom scripts according to their specific needs and preferences.
- Security: it allows you to configure firewall rules, establish secure VPN connections, and implement encryption mechanisms to protect the network from unauthorized access.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend DD-WRT because it offers versatile features like multiple wireless SSIDs, enabling various wireless networks with different security levels. It also provides network storage options for file sharing. DD-WRT's high level of customization lets users adjust it to fit their unique requirements.
Another advantage of DD-WRT is that it is compatible with a wide range of hardware platforms. It may be installed on a variety of routers, including older models, making it a low-cost solution to repurpose existing equipment. The security features of DD-WRT are also well-known. It receives regular updates to address security vulnerabilities and offers network security capabilities such as packet filtering, NAT, and VPN.
DD-WRT is free to use and distribute as open-source software. However, some hardware manufacturers charge a price for pre-installed firmware versions. Also, there are several disadvantages to utilizing DD-WRT. One potential disadvantage is that installation and configuration require considerable technical knowledge. It may be difficult to set up for users who are unfamiliar with networking fundamentals or Linux.
Another disadvantage of DD-WRT is the absence of official support. There is no official customer service team, but there is an active community of developers and users that provide assistance and guidance. This can be a problem for folks who need help with their router.
Who is it recommended for?
DD-WRT is recommended for networks of all sizes, from small setups to larger ones, thanks to its flexibility, ability to work with older hardware, and robust security features. Experts in networking often choose DD-WRT for its customization options, which include the ability to add new features or tweak existing ones using plugins and add-ons, making it a versatile tool for various networking needs.
Pros:
- Extreme Features: DD-WRT offers a wide range of advanced features that go beyond what you typically find in standard router firmware.
- Enterprise-Class Monitoring Support: It provides robust monitoring capabilities, allowing for detailed tracking and management of network activity.
- Good Throughput: DD-WRT can often deliver high network performance. Hence, it is perfect for demanding tasks like streaming or online gaming.
- Very Stable: It is reliable and stable, providing consistent performance over time.
Cons:
- Drop in Speed: Some users have reported a noticeable decrease in internet speed when using DD-WRT compared to the original firmware provided by the router manufacturer.
It is a popular choice for both small and big networks due to its customizability, compatibility with older hardware, and security features. Users should be aware of the potential drawbacks, such as the requirement for technical expertise and the lack of official support.
4. VyOS
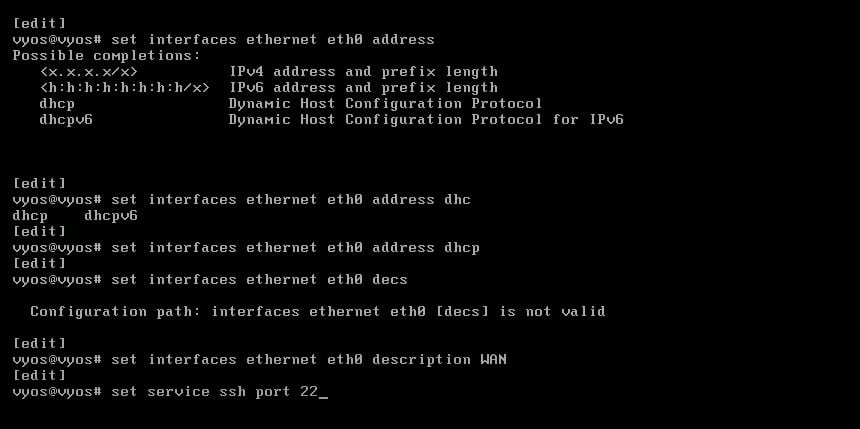
VyOS is a Debian Linux-based open-source router and firewall platform. It has a variety of features and functionalities, making it a popular choice for both small and large networks. VyOS's excellent routing capabilities are one of its most notable characteristics. It contains complex routing protocols such as OSPF, BGP, and RIP, making it a complete network routing solution.
Key Features:
- High-Availability: With features like VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) and clustering, it offers uninterrupted connectivity for critical network services.
- NetFlow/sFlow Sensor: By collecting and analyzing flow data, VyOS provides insights into network usage patterns, bandwidth consumption, and potential security threats.
- Stateful Load Balancing: VyOS offers stateful load balancing capabilities, distributing network traffic across multiple servers or links based on predefined criteria.
- Network Services: These built-in services are capable of handling a wide range of networking tasks and requirements, from simple routing to complex network configurations.
Why do we recommend it?
VyOS can be installed on various hardware types like physical servers, virtual machines, and cloud platforms. Additionally, it can be deployed as a virtual appliance, simplifying testing and evaluation processes. This adaptability makes VyOS an excellent choice for organizations looking for a versatile and scalable router operating system to meet their networking needs.
VyOS has several security features in addition to routing. It provides stateful firewalling, VPN, NAT, and other features to assist secure networks. VyOS also supports QoS, network address translation, and other advanced features, making it a versatile solution.
VyOS is also well-known for its adaptability. It is a suitable alternative for a variety of situations because it may be deployed as a virtual machine, on bare metal hardware, or as a cloud instance. Its web-based interface is also user-friendly and straightforward, making configuration and management simple.
VyOS is free to use and share as open-source software. Commercial support and services are, however, available for individuals who require further assistance or features. VyOS has the potential disadvantage of requiring more technical expertise to set up and customize than other router software solutions.
Who is it recommended for?
VyOS is recommended for network experts and professionals needing advanced routing capabilities and robust security features. Its support for protocols like OSPF, BGP, and RIPv2, along with VPN options such as IPsec and OpenVPN, make it ideal for complex networking setups. Additionally, VyOS offers advanced firewall functionalities like stateful packet inspection and zone-based firewalling, catering to the needs of organizations requiring high-level network security and management.
Pros:
- Powerful Networking Features: VyOS offers a wide array of networking capabilities, including routing, firewalling, VPN, and more. It's like having a Swiss Army knife for your network.
- Flexible and Customizable: You can tailor VyOS to fit your specific networking needs. Whether you're a home user, a small business, or an enterprise, VyOS can adapt to your requirements.
- Stability and Reliability: VyOS is known for its stability and reliability. It's built on a solid foundation, making it suitable for mission-critical environments where uptime is crucial.
- Active Community and Support: There's a vibrant community of users and contributors around VyOS. You can find help, tutorials, and documentation online, as well as engage with other users for advice and support.
Cons:
- Hardware Compatibility: While VyOS supports a wide range of hardware, not all devices are compatible. You'll need to check the hardware compatibility list to ensure that VyOS runs smoothly on your chosen hardware platform.
While the web-based interface is simple to use, users may need to spend more time configuring the product to match their individual requirements. Another potential disadvantage of VyOS is that it may require more hardware than other router software solutions, which may limit its usability for some users. Many users like it because of its sophisticated routing capabilities, advanced security features, and versatility. However, before using VyOS, users should be aware of the potential need for technical expertise as well as greater hardware requirements.
5. RouterOS
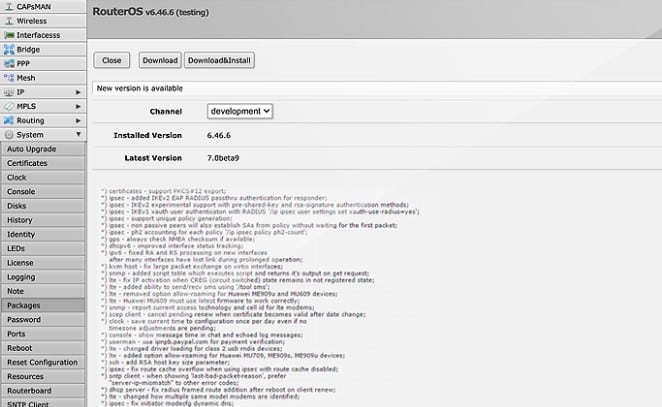
MikroTik, a Latvian networking firm, created RouterOS, a robust router operating system. It has a variety of features and functionalities, making it a popular choice for both small and large networks. RouterOS' flexibility is one of its most notable qualities. It may be used as a router, firewall, hotspot gateway, and more, making it a complete network management solution.
Key Features:
- Advanced Routing Protocols: These protocols enhance network scalability, reliability, and performance by automatically adjusting routing tables based on network topology changes.
- QoS Support: With QoS, users can allocate bandwidth resources to critical applications, ensure low-latency communication for real-time services, and optimize network performance by managing traffic congestion effectively.
- Intuitive Interface: With a user-friendly design and easy-to-navigate menus, RouterOS enables users to configure routing, firewall, and other network settings efficiently.
Why do we recommend it?
RouterOS is recommended for its advanced networking capabilities. With features like Quality of Service (QoS), network address translation (NAT), and VPN support, it enhances network performance and security. Moreover, RouterOS supports advanced routing protocols like OSPF, BGP, and VRRP, making it perfect for intricate network configurations. Whether for small businesses or large enterprises, RouterOS offers the tools needed to manage and optimize network operations efficiently.
RouterOS also incorporates sophisticated technologies like BGP, OSPF, MPLS, and VPLS, making it a formidable routing solution. It also incorporates several security capabilities, including stateful firewalling, VPN, and others, to aid with network security. Furthermore, RouterOS supports QoS, network address translation, and other advanced features, making it a versatile solution. RouterOS may have a longer learning curve than other router software solutions, which could be a disadvantage. While its web-based interface is simple and easy to use, it provides a vast range of customizable options that may necessitate more technical knowledge to fully exploit.
RouterOS has a variety of pricing choices based on the features and functions required. The program can be licensed for specific hardware or usage as a virtual machine. For individuals that require more assistance in utilizing the software, MikroTik also provides a variety of training and certification opportunities. Another potential disadvantage of RouterOS is that it may require more specific hardware than other router software solutions, which may limit its use for some users.
Who is it recommended for?
RouterOS is recommended for individuals and businesses seeking a versatile networking solution. Experts in IT and networking often use this tool due to its ability to transform a PC into a fully-featured router with essential functions like routing, firewall, and bandwidth management. It also offers advanced features such as a wireless access point, VPN server, and hotspot gateway.
Pros:
- Dual Stack IPv4 – IPv6: RouterOS supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, which means you can seamlessly transition to the newer IPv6 standard while still supporting existing IPv4 devices on your network.
- Easy Management: RouterOS is easy for users to configure and monitor their network settings without needing advanced technical knowledge.
- Multiple Secure Connection Options: It offers various secure connection options, such as VPN (Virtual Private Network), SSH (Secure Shell), and SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), to ensure the integrity of data transmitted over the network.
Cons:
- Administration Dashboard: Some users find the administration dashboard of RouterOS to be less intuitive; this can make navigation and configuration more challenging for users who prefer a more user-friendly interface.
RouterOS is a versatile and powerful router operating system with a variety of features and functionalities. Many customers like it because of its adaptability, comprehensive routing and security capabilities, and support for QoS and other complex functions. However, before using RouterOS, customers should be aware of the potential need for technical expertise as well as greater system requirements.
6. Tomato
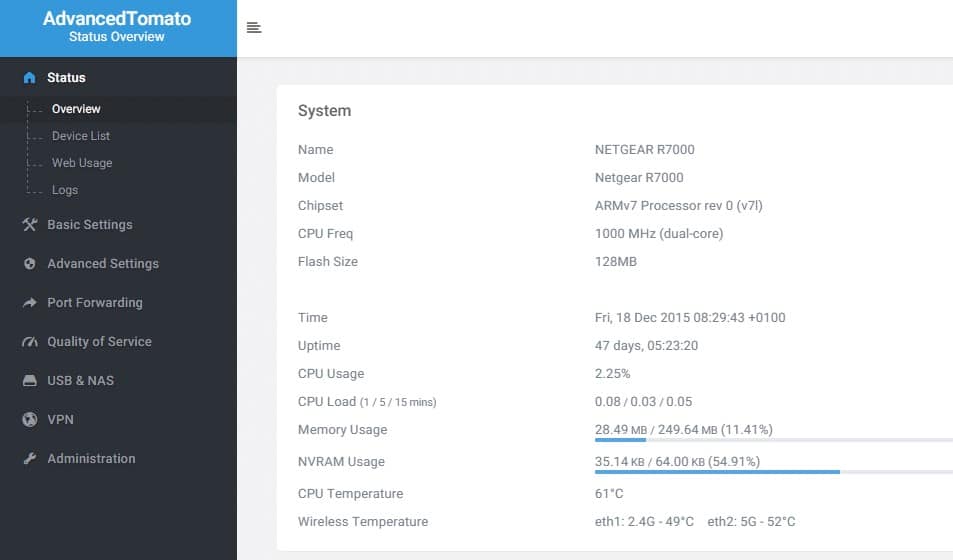
Tomato is a free and open-source router operating system with a variety of features and functionalities for controlling small to medium-sized networks. Tomato's straightforward web-based interface is one of its main features, making it simple for customers to set up and administer their networks.
Key Features:
- Wireless Client Station (STA): This enables the router to access the internet wirelessly, extending network connectivity without the need for additional wiring or infrastructure.
- Wireless Ethernet (WET) Bridge: Tomato offers Wireless Ethernet (WET) bridge functionality, allowing multiple wireless routers or access points to connect to each other wirelessly.
- Wireless Distribution System (WDS): This feature allows for the creation of more extensive wireless networks, providing extended coverage and improved connectivity for wireless devices.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Tomato for its lightweight, open-source firmware designed for Broadcom-based routers. It boasts a user-friendly interface and advanced features like bandwidth monitoring, QoS, and access restrictions. With capabilities such as WDS, wireless client modes, and script customization, Tomato offers enhanced wireless functionality. It also supports telnet/SSH connections, custom script execution, and wireless site surveys. For users seeking a versatile and feature-rich alternative firmware, Tomato stands out as a top choice.
Tomato, in addition to its user-friendly interface, includes several complex capabilities such as Quality of Service (QoS), VPN support, and traffic monitoring. These qualities combine to make it an effective solution for regulating network traffic and ensuring that key applications have adequate bandwidth. Tomato also supports a variety of wireless gear, including popular versions from vendors such as Linksys, Buffalo, and Asus. As a result, it is a versatile choice for customers that need to manage both wired and wireless networks.
Tomato may not have as many advanced capabilities as other router operating systems on the market, which could be a disadvantage. While it supports QoS, VPNs, and other advanced capabilities, it may not be the ideal choice for users who require more advanced routing or security. Tomato can be downloaded for free, and there are no license fees associated with its use. As a result, it is a cost-effective alternative for customers who need to manage small to medium-sized networks.
Who is it recommended for?
Tomato is recommended for individuals and businesses requiring management of both wired and wireless networks. It's compatible with a range of wireless gear from vendors like Linksys, Buffalo, and Asus, offering versatility in network setup. Experts in networking often use Tomato for its ability to handle diverse network environments.
Pros:
- Stability: Tomato firmware is known for its stability, making it a reliable choice for average users. It performs well even on under-powered routers.
- Ease of Configuration: Setting up Tomato firmware is straightforward and user-friendly. Its simplicity makes it accessible to users who may not be tech-savvy.
- Less Code, Fewer Bugs: Tomato's firmware has less code compared to other alternatives like DD-WRT. This results in fewer bugs and a more stable performance overall.
- Reporting Capabilities: Tomato offers useful reporting features such as real-time traffic monitoring, statistics, and logs for inbound and outbound connections, providing users with valuable insights into their network activity.
Cons:
- Limited Router Compatibility: Tomato firmware is not compatible with as many routers as some other firmware options, like DD-WRT.
Overall, Tomato is a user-friendly and adaptable router operating system with a variety of features and functions for network management. Its user-friendly interface, compatibility with a wide range of wireless gear, and support for QoS and other advanced features make it a popular choice among many users. Users should be cautious, however, of its potential limits in advanced routing and security features.