Our funding comes from our readers, and we may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
The Definitive Guide to ITIL

UPDATED: March 31, 2022
The role of any IT professional is to design, create, manage, and support the end-to-end delivery of IT services, ranging from cloud services, backups, network security, training, and help desk support. If IT teams are quickly overwhelmed, can’t adapt to change, or can’t solve IT service failures efficiently, the overall business may be compromised and fail.
Having a set of practices in IT service management that allows ITs to monitor, shape, optimize, and improve the IT services or simply make their lives easier is paramount. And this is where ITIL comes into place.
In this definitive guide to ITIL, we’ll go through the definition of the ITIL framework. You’ll learn about ITIL’s history along with some of its key benefits and drawbacks. In the later sections, we’ll go through the descriptions of ITILv3, ITILv4, and its certifications.
Table of Contents
- What is ITIL?
- ITIL vs ITSM? What are the differences?
- A brief history of ITIL
- Business benefits of ITIL
- The drawbacks of ITIL
- ITILv3 – The five stages of ITIL Lifecycle
- ITILv4
- ITIL Certifications
- Final words
1. What is ITIL?
ITIL or Information Technology Infrastructure Library is a framework designed to improve efficiency and achieve better results with the IT services delivery within an organization. The framework aims to standardize the selection, planning, maintenance, and delivery. In other words, it standardizes the overall lifecycle of the IT services to improve the clarity, predictability, flexibility, quality, and knowledge retention within the organization.
Since IT and its administrators are an integral part of any business and have a major role in its success and progress, they must be treated as so. The ITIL framework ensures that the entire IT doesn’t remain as back-end supporters; Instead, it ensures that the IT is viewed as business partners.
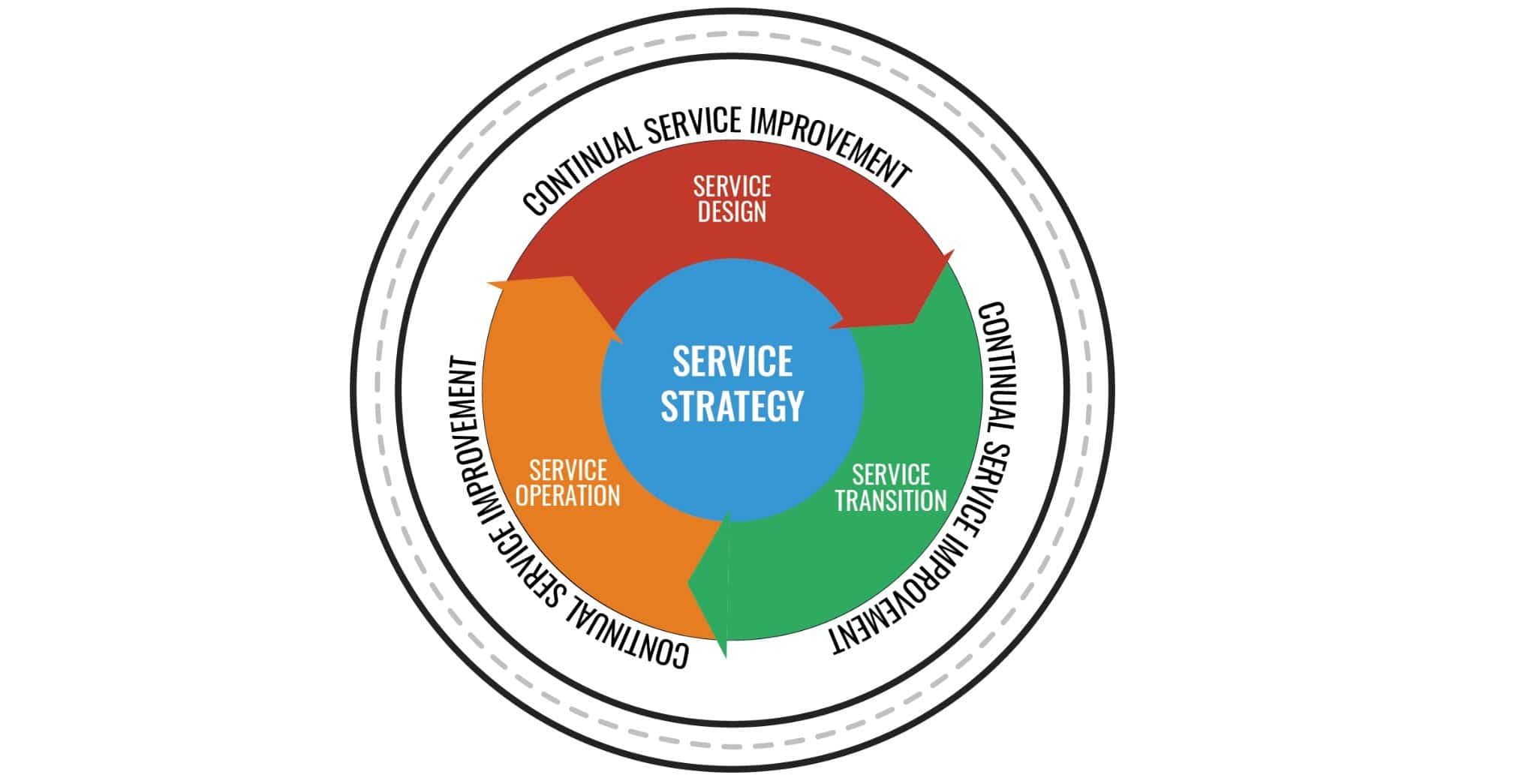
The last version of ITIL is ITIL v3. This latest version consists of the following five phases: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
2. ITIL vs ITSM: What are the differences?
Many people get confused with ITIL or ITSM, and they use the terms interchangeably. Although both terms are interrelated, ITIL and ITSM are not the same. So, what is ITSM, and how is it related to ITIL?
What is ITSM? ITSM or Information Technology Service Management defines how IT services are managed efficiently. The core characteristics of ITSM are IT services, customers, SLAs, and processes. Many times companies don’t realize that they are doing ITSM, but the fact is whenever and wherever IT systems and IT infra come into the scene, ITSM is applied inevitably.
So, what’s the difference between ITIL and ITSM?
- ITSM is how you manage the IT services you deliver. ITSM encompasses other frameworks and certifications like COBIT, ISO/IEC 2000, Microsoft MOF, IBM, ITPM, and ITIL. The former (ITIL) is the most popular approach to ITSM.
- The ITIL framework is simply one of the ways to manage your IT service or to efficiently implement ITSM. ITIL enables companies to achieve efficient ITSM at their premises.
3. A Brief History of ITIL
Currently, the ITIL framework has four versions released from time to time with iterations to ensure that the framework adopts the latest circumstances or challenges of the IT industry. ITIL updates enable the framework to be effective and revised as in current times.
ITIL’s Timeline
- 1989: First Publications of ITIL
- 2000: Publication of ITILv2
- 2007: Publication of ITILv3
- 2012: Publication of ITILv3 edition 2011
- 2019: Publication of ITILv4
The era of ITIL started in the 1980s when the world saw decentralized data centers spread geographically across subcontinents. This decentralization led to discrepancies in different IT deployments, which ultimately caused poor IT performance.
So, as a solution for bringing consistency for IT practices across the entire IT service lifecycle of an organization, the United Kingdom’s Central Computer and Telecommunication Agency (CCTA) developed Government Information Technology Infrastructure Management (GITIM) which released the first version of ITIL (ITILv1) in 1989.
A decade later, in 2000, the CCTA firm became the Office of Government Commerce (OGC), and in 2001, the newly established firm released ITILv2. In 2007, the same firm released ITILv3. In 2011, released an update of the same ITILv3, which gave it the name of ITIL 2011 v3. Although no new concepts were added to ITIL 2011, the updates resolved some errors and inconsistencies (related to text and diagrams) across the entire framework. Although ITIL v3 is the basis of ITIL 2011, the former ITIL v3 is no longer offered.
As of this day (Feb 2022), we have the latest ITIL version, ITILv4, which is managed and developed by the global best practice company, Axelos. Axelos released the latest ITIL guidelines in 2017 and updated them throughout 2019 and 2020.
4. Business Benefits of ITIL
ITIL is the framework that lays the foundation for successfully implementing the best IT practices or ITSM. Such best practices, in turn, let IT teams and admins have more confidence, be more efficient, improve their role, and deliver better customer experiences.
Now, let's look into the detail about the ITIL business benefits:
- Cost optimization ITIL ensures that the time and resources within an organization are prioritized and used efficiently based on the business and customer requirements. Optimizing time and resources will ultimately help achieve higher productivity and cost savings.
- Higher customer satisfaction If the service quality and delivery of an organization improve, customer satisfaction will also improve, which in turn will result in longer customer retention. When customers are happy with an organization's services and capabilities, they are likely to remain loyal, help improve the brand's popularity and grow revenue.
- Better risk management ITIL's v4 risk management helps identify, assess, and manage risk. ITIL's risk management practices, including continual improvements, problem management, information security management, and more, help IT admins spot trouble, have fewer surprises, and remain focused.
- Alignment of business goals ITIL ensures that the IT teams function actively as business partners rather than behaving like back-end supporters. For the successful functioning of a business, the goals of the IT department should be the same as the goals of the entire organization. So, ITIL aims to achieve the same by recognizing IT as an integral part of a business.
5. The Drawbacks of ITIL
Despite the several benefits of ITIL mentioned in the previous section, ITIL also has some drawbacks.
- Optimal implementation of ITIL requires training and staff expertise, resources that can be time-consuming and costly. The implementation on a more advanced level for better results may take months, if not years. So, there are no shortcuts or short-term effects with ITIL efforts.
- ITIL initiatives may interfere with your existing process and IT infrastructure (and vice versa). And since ITIL takes a reasonably long time to fully mature, there are chances that other project initiatives, if carried out in the way of ITIL, also disrupt the ITIL implementation. A typical task for an IT admin may take a couple of minutes, but with an immature ITIL implementation, it may take hours.
6. ITILv3 – The five stages of ITIL Lifecycle
The ITILv3 defines the ITIL service lifecycle into five different stages with their ITIL implementation methodology organized in the five respective publications: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
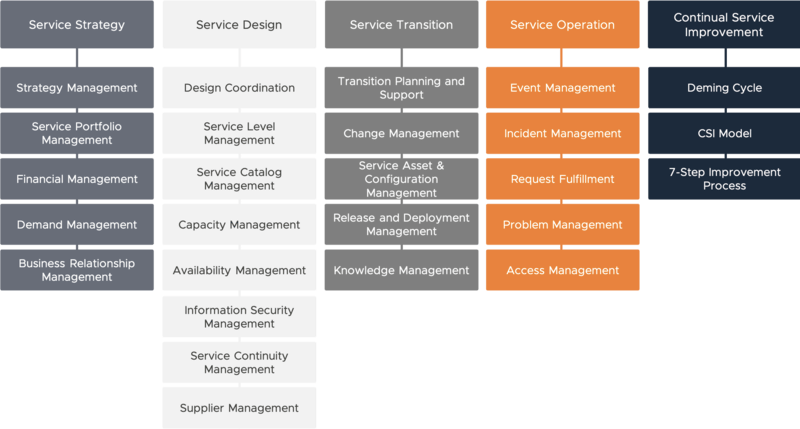
The ITIL core publications are as follows:
The following five core ITIL books are a type of series publications, designed to be read together.
- Service Strategy This publication defines how IT can align the goals of the business and customers to maximize the benefits of ITIL.
- Service Design The service design publication advises on designing the IT policies and documentation production.
- Service Transition The service transition book provides advice on the transition or changes of ITIL implementation and releases practices.
- Service Operation The Service Operation describes how to manage IT Services daily, monthly, and yearly for robust ITSM.
- Continual Service Improvement This book covers how to introduce updates regarding improvements and policies inside the ITIL framework.
Although the ITIL V3 process remains effective, widely used, and popular, everybody now has access to the latest ITIL version, the ITILv4.
7. ITILv4
Previous ITIL versions focused on processes. But now ITILv4 changed the focus to practices. Management practices are one of the key components of ITILv4. Management practice is a set of resources from an organization designed to accomplish a goal.
ITIL v4 covers 34 practices divided into three main categories: General Management Practices, Service Management Practices, and Technical Management Practices. These categories are mapped to service value chains and systems.
- General management practices This ITITLv4 category describes projects and portfolios, enterprise risk, information security, continual improvement, workforce and talent, relationships, and suppliers.
- Service management practices This category defines business analysis, service design and continuity, service desk, monitoring and incident management, change enablement, and IT asset management.
- Technical management practices This ITITLv4 category covers software development, deployment, infrastructure, and platform.
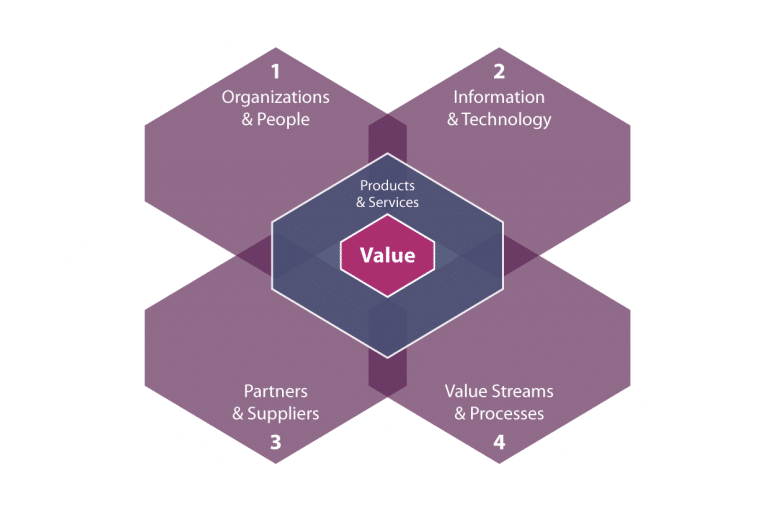
As you can see from the image below, the ITILv4 is based on a four-dimensional framework.
- Organizations and People
- Information and Technology
- Partners and Suppliers
- Value streams and Processes
These four dimensions are vital components to create high-quality products and services, which ultimately deliver value to customers.
8. ITIL Certifications
To become an ITIL expert, you will have to enroll in ITIL programs and pass the ITIL certifications.
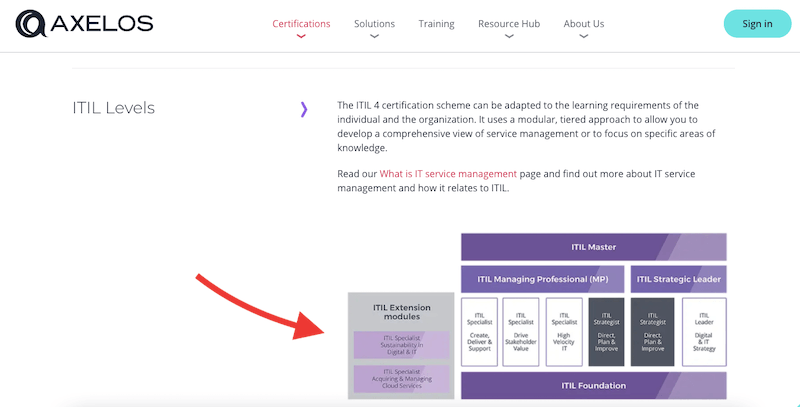
Axelos, the company behind ITIL, PRINCE2, and other world-renowned best practice certifications and methods is officially in charge of all ITIL Certifications. The ITILv4 certification scheme is based on five levels: Foundation, Practitioner, Intermediate, Expert, and Master.
Let's learn about each of these ITIL Certification levels in brief
- Foundation Level As the name suggests, the ITIL Foundation Level covers the basic concepts of the ITIL Lifecycle and its implementation practices. It introduces the operating model for creating, delivering, and continually improving technology products and services.
- Practitioner Level The next level is the Practitioner Level. This certification provides practical guidelines on adapting the ITIL framework to fulfill business objectives. It opens the doors for beginners to become full practitioners. They no longer speak the ITIL language, but they put it into practice.
- Intermediate Level The Intermediate Level certification is designed on a modular structure, where each module puts a different focus on ITSM. It is divided into two distinct categories of ITIL management processes: Service Lifecycle and Service Capability modules. These two modules cover the ITILv4 principles, processes, and activities.
- Expert Level The ITIL Expert's level certification is designed for those with high knowledge and skills on the entire ITIL scheme. In order to be eligible for the ITIL Expert Level Certification, you must qualify for the Practitioner and Intermediate Level programs. You will need the ITIL Expert certificate to progress to the ultimate certification level, the ITIL Master.
- Master Level The final ITIL level for certifications is the Master Level. This certification demands an individual to have an in-depth understanding of the ITIL Management processes and implement ITIL in their respective organizations. So, a master-level holder has hands-on experience in ITIL adoption and project execution.
Final Words
ITIL is a globally-recognized leader in IT Service Management. It lays the foundation for successfully implementing ITSM into any organization. ITIL does not only benefit businesses but also IT admins and customers. But still, implementing ITIL does take resources, and if it is correctly implemented, it may lead to workflow deficiencies.
Aside from getting certified, you may need tools to assist you in implementing ITIL's best practices. Some of the best ITSM software tools in the market are SolarWinds Service Desk, Atera Helpdesk Software, Freshservice, and ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus.