Our funding comes from our readers, and we may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Guide to AS2 Protocol and differences to SFTP
UPDATED: October 23, 2023
How do sensitive industries like commercial airlines, healthcare, or transport talk to each other and share data? How do they transfer structured B2B data securely and reliably over risky networks like the Internet? The answer is the AS2 protocol.
In this guide to AS2 protocol, we’ll learn everything about this popular transfer mechanism, from its background, its benefits, its functionality, how it works, and a comparison with SFTP.
Here is our list of the best Applicability Statement 2 (AS2) tools:
- SolarWinds Serv-U Managed File Transfer (MFT) – FREE TRIAL: A versatile multi-protocol remote file sharing solution that excels in control and security of data transfers. It stands out with its support for various protocols and easy-to-use features like drag-and-drop transfers.
- Files.com – FREE TRIAL: This cloud-based file management solution shines with its seamless integration with popular file-sharing services and robust security measures, making it ideal for businesses of any size.
- ArcESB: ArcESB is renowned for its comprehensive support for B2B messaging protocols and seamless integration with business applications, providing a clean and efficient user interface.
- Fortra GoAnywhere MFT: Distinguished by its NIST-certified encryption and wide range of supported protocols, GoAnywhere MFT is a strong contender for organizations prioritizing security and compliance.
What is AS2
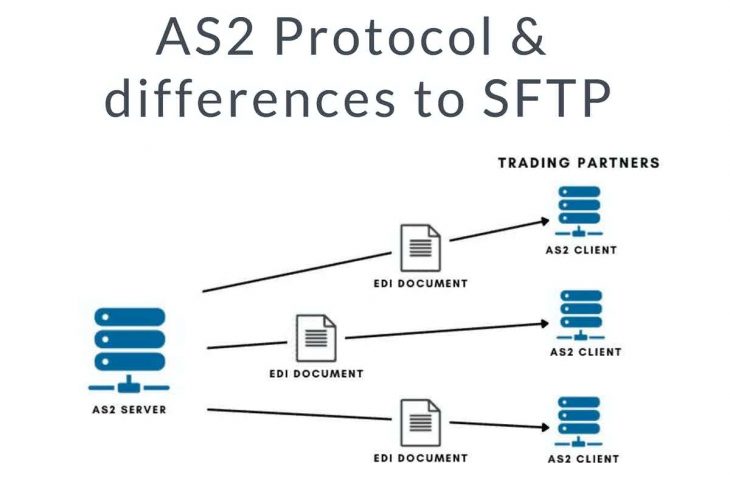
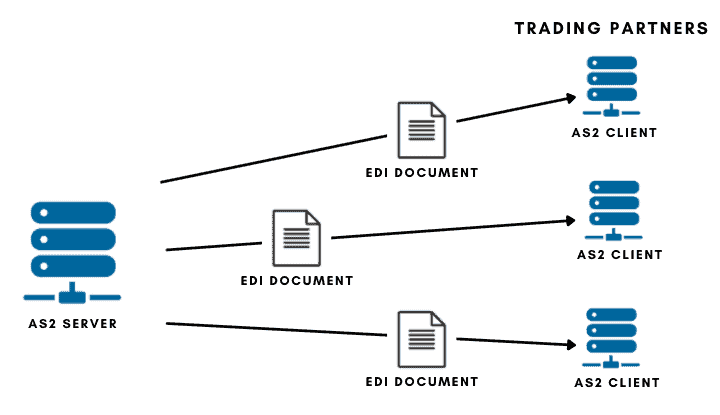
The Applicability Statement 2 (AS2) is a type of file transfer mechanism based on HTTPS (Hypertext Transport Protocol Secure) and S/MIME. AS2 can be used for transferring any file, but it is commonly used for EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) documents within B2B environments.
As a protocol, AS2 defines a safe procedure to establish a point-to-point connection between an AS2 client and an AS2 server in any type of network, including public networks like the Internet. AS2 uses digital certificates and encryption to provide security for transferring sensitive information like EDI documents across risky networks.
Background
AS2 was created by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 2002 and is specified in the RFC 4130. AS2 is a second-generation protocol aimed to replace the Applicability Statement 1 (AS1), built in the 1990s and was based on email protocols. AS2 was designed based on AS1, with the same encryption and some Message Disposition Notification (MDN) conventions.
Walmart, the US-based retail giant, was one of the first to adopt AS2 for their EDI communications. It required all of its suppliers and vendors to also use the same protocol for exchanging information related to consumer goods. After Walmart adopted AS2, other giants such as Target, Amazon, Lowe’s, and many more also followed.
Today more industries are starting to use the AS2 protocol, especially for their EDI transactions. AS2 is widespread within the healthcare industry, as it is compliant with HIPAA.
The Benefits of using AS2
AS2 can be a fantastic solution for safe, fast, and large-size data transfers. Due to its security and non-repudiation mechanisms, the AS2 protocol can even require some B2B EDI document transfers.
Some of its benefits
- Use as an alternative to expensive VANs AS2 is being used as an alternative option for expensive Value Added Networks (VAN). When exchanging EDI documents, third-party VANs require a service subscription that is generally priced based on data volume. The AS2, on the other hand, only requires AS2-based software and the Internet.
- Have a wider reach Since big US-based retail companies like Walmart and Lowe’s started to use AS2 to share EDI documents, the protocol is becoming almost a de facto standard across a wide range of suppliers and partners. Being able to use EDI with the Internet and lower costs allow more organizations to interconnect. AS2 works as long as organizations agree and use AS2 to transfer data using the Internet.
- Interoperable AS2 is payload-agnostic. It can be used to transfer any file or document, including standardized formats such as EDIFACT, X12, and XML. Both the AS2 sender and the AS2 receiver need to operate AS2. But fortunately, the list of transaction partners supporting AS2 is growing exponentially, especially within retail.
- Support for SSL and S/MIME AS2 sends data across the Internet using the HTTPS (HTTP over SSL) protocol. HTTPS adds a layer of SSL encryption to protect the traffic. In this way, the AS2 messages are sent via an SSL encrypted tunnel across the Internet. AS2 also protects EDI data at the payload layer, using the S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) based on asymmetric cryptography. The standardized S/MIME message wraps the EDI data inside a secure envelope to ensure safe file transmission.
- Data Integrity AS2 also ensures the integrity of the data and identity of the sender using digital certificates. The receiving end sends a receipt back to the sender to ensure the message was delivered correctly. These receipts are signed using the digital certificate and sent back along with a checksum value using Message Integrity Check (MIC).
- Non-repudiation AS2 uses a return receipt notification service known as Message Disposition Notification (MDN). The AS2 message sender may request the receiver an MDN receipt informing on the successful delivery of the message. An MDN receipt tells whether the AS2 transfer was completed successfully, and the message arrived without change. AS2 has several options, including:
- MDN can be synchronous if the receipts are sent back immediately.
- MDN can be asynchronous if the receipts are sent back at a later time. MDN async mode can be sent back via email.
- May put for no MDN return. The recipient can choose not to send an MDN.
- Filename preservation feature. MDN may contain the filename of the trading partner.
How Does AS2 work
As said before, AS2 works using the client/server model. Both sides (sender and receiver) need to support AS2. The AS2 specifies the procedure, including compression, signature, and encryption.
The content of the files transferred by AS2 (or payload) is not specified by AS2 but by a standardized format such as EDIFACT, X12, or XML. If AS2 is used for EDI, before sending documents over AS2, they need to be prepared in the EDI format (mapped or translated).
Message Flow
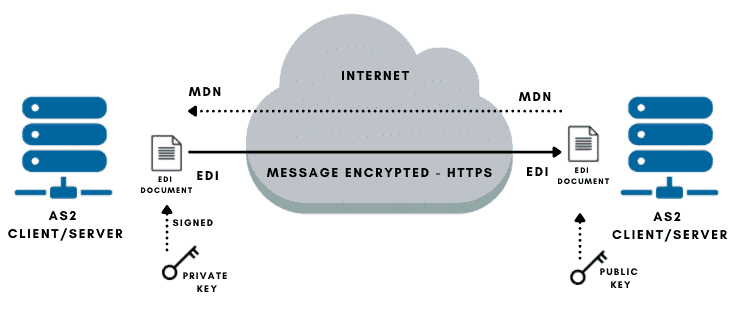
- AS2 creates an encoded envelope of the EDI document using the S/MIME protocol.
- The EDI envelope (S/MIME data) gets compressed and signed by the AS2 sender platform. Singing is the action of encrypting a hash using a private key. This results in a digitally signed data (certificate) that attaches to the original data. This signed data helps the recipient confirm the sender’s authenticity (and vice versa).
- To ensure integrity, the AS2 message sender also calculates a checksum of the message using the Message Integrity Check (MIC), with either MD5, SHA-1, or SHA-2 hashing algorithms. It places the MIC value into the message (again, using the private key).
- A request for receipt (MDN) is attached to the message.
- Encrypted. The message gets SSL-encrypted and transmitted through the Internet.
- The message arrives at the destined AS2 platform. The message gets SSL-decrypted, decompressed, and the sender’s digital signature gets verified by the recipient using the public key. The MIC value is also demonstrated.
- The AS2 non-repudiation phase starts. If requested, an MDN receipt along with a digital signature is sent back to the original sender.
- The sender receives the MDN and verifies the receipt’s digital signature. When received, the sender can verify the MDN signature to ensure that the recipient got the message.
- The AS2 sender processes the MDN. The sender validates the receipt MDN signature. A failed MDN is sent back from the recipient if there was a problem while receiving the AS2 message. In addition, if the sender requested and did not receive an MDN, the sender may treat this as a failure. The sender also compares the returned MIC with the original.
AS2 vs. SFTP
Although AS2 and SFTP can transfer EDI documents, they are two quite distinct file transfer protocols.
Now that you know what AS2 is and how it works, let's define what SFTP is.
SFTP (FTP over SSH) is a secure FTP alternative to the traditional and insecure FTP (File Transfer Protocol). It uses a client/server model to establish a Secure Shell (SSH) connection and share data across the Internet or any other network. This protocol was designed as an extension of SSH ver 2.0 to provide file transfers. SFTP goes beyond the standard, secure file transfer, as it also allows a range of additional operations, including remote file access and management and file transfer pause/resume.
AS2 and the differences to SFTP
Encryption
- AS2: uses digital certificates, encryption, and hashing algorithms. The messages that are sent over with AS2 are encrypted, compressed, and signed. AS2 can also encrypt the payload itself, using the S/MIME cryptographic technology. And AS2 uses hashing processes to ensure file integrity.
- SFTP: All the file transfers in SFTP are run over an SSH secure channel. In other words, SFTP inherits all security features from SSH, a protocol that supports symmetric encryption mechanisms like AES or the deprecated 3DES.
Authentication
- AS2: AS2 can authenticate using digital certificates. An AS2 server has a digital certificate with a public key that belongs to the client’s private key. AS2 can also authenticate transactions using a username and password.
- SFTP: Access to files via SFTP can be protected with a username and password or an SSH key. SFTP can be used with dual-factor authentication to enhance security—or a combination of password and SSH key. An SSH server uses public-key cryptography to authenticate clients holding a private key.
Non-repudiation of receipt
- AS2: uses MDN of receipt to ensure that the transferred message has been sent and received by the right parties. Users can request an MDN of receipt, which is signed (with a certificate) and returned when the other party has received the message.
- SFTP: SFTP does not have non-repudiation mechanisms.
Interoperability and ease of use
- AS2: It requires a higher maintenance overhead, special software, and technical expertise. All these requirements end up increasing the cost for implementation.
- SFTP: It is easier to implement, operate, and it is cheaper. SFTP is based on port 22 (but can be assigned others) for establishing a connection, authentication request, tunneling, issuing commands, and exchanging data. SFTP is supported by a wide range of software and platforms, and it is easily implemented on any firewall.
Our methodology for selecting the Best Applicability Statement 2 (AS2) Tools:
We've broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- Focus on multi-protocol support, including AS2, SFTP, FTPS, and HTTPS.
- Evaluation of the ease of file sharing and synchronization capabilities.
- Importance of compliance with security standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA.
- Assessment of integration capabilities with existing systems and third-party services.
- Prioritizing tools that offer robust security features, including encryption and 2FA.
- Consideration of user-friendliness, particularly for non-technical users.
The Best Applicability Statement 2 (AS2) Tools
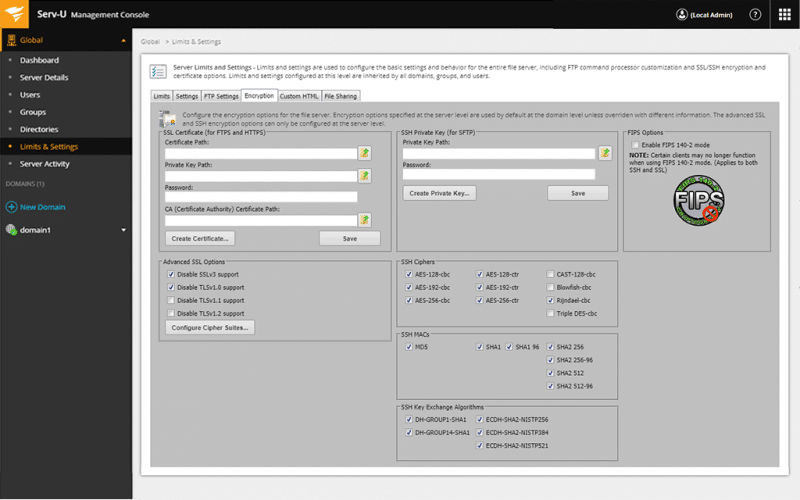
1. SolarWinds Serv-U Managed File Transfer (MFT) – FREE TRIAL
Serv-U MFT is a multi-protocol remote file sharing solution that improves the control and security of internal and external file transfers. It supports file transfers from protocols like FTP, HTTP, FTPS, SFTP, and HTTPS.
Key Features:
- Peer-to-peer transfers using web browsers or mobile devices
- Request and send files on an ad-hoc basis
- Ensure data-in-transit compliance with PCI DSS, HIPAA, FISMA, SOX, and others
- Transfer large-size files and synchronize them anytime
- Authentication through Active Directory or database
Serv-U MFT is designed for businesses of all sizes that need secure data transfers. An alternative for smaller companies is Serv-U FTP that allows transfers over SFTP.
Pros:
- Supports FTP, FTPS, and SFTP file transfers, making it a more flexible option than some of its competitors
- Robust search features are ideal for large file transfers over long periods of time
- Built with the enterprise in mind
- Supports drag and drop transfers, making it an easy option for end-users
- Built-in schedule works well for EDI and other regular transfers
Cons:
- Would like to see a longer trial period for testing
SolarWinds Serv-U Managed File Transfer (MFT) is available to test out for a fully functional 30-day free trial.
2. Files.com – FREE TRIAL
Files.com is a cloud-based file management solution. It allows users to transfer and share files using a cloud server while encrypting files in transit (and at rest). Files.com is popular because it will enable third-party integration of popular file-sharing mechanisms, including SFTP, WebDAV, HTTPS, cloud storage (AWS, Azure, etc.), and allows you to manage them from a single dashboard.
Key Features
- Share files via share links or file inboxes
- 2FA and encryption at rest
- Supports files up to 5TB in size
Pros:
- Cloud-based service with no lengthy onboarding process or complicated setup
- Cloud storage provides scalable storage and features without needing an on-premise setup
- Support file redundancy and backup
- Integrates well with other services like Dropbox or Google Drive, giving it more flexibility than similar products
- Takes security seriously, enforces 2FA
- Subscription tiered pricing makes this an accessible solution for any size business
Cons:
- The platform offers many different features, which can require a time investment to learn them all
Files.com is a subscription-based service, offered on full 30-day free trial.
3. ArcESB
ArcESB is a popular platform used for EDI communications and Managed File Transfer (MFT). It supports the most critical B2B messaging protocols, such as AS2, OFTP, X12, EDIFACT, XML, and more. In addition to managed file transfers, ArcESB allows the preparation and management of EDI documents, including mapping and translation.
Key Features
- Drummond Certified solution for AS2 file transfer and messaging
- End-to-end integration with applications, including ERPs, CRMs, and more
- B2B automation
Pros:
- Built for the enterprise with EDI as a core feature
- Offers a wide range of B2B protocols including AS2, X12, and OFTP
- Offers a clean interface that’s easy to work in
- Includes a suite of automation tools
Cons:
- Not designed for non-enterprise orginizations
4. Fortra GoAnywhere MFT
GoAnywhere MFT from Fortra is a secure file transfer solution for multiple protocols, including SFTP, FTPS, HTTPS, and AS2. GoAnywhere supports various encryption protocols and offers a NIST-certified FIPS 140-2 Validation encryption module.
Key Features
- Drummond Certified for AS2
- Supports SHA2 algorithms
- Integrated clustering support
- A Key and Certificate Management System (KMS)
Why do we recommend it?
Fortra GoAnywhere MFT stands out as a highly secure file transfer solution, supporting multiple protocols like SFTP, FTPS, HTTPS, and AS2. Its emphasis on security is evident in its NIST-certified FIPS 140-2 Validation encryption module. The Drummond Certification for AS2 compliance ensures reliable and secure AS2 file transfers, making it a trustworthy choice for businesses prioritizing data security.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for organizations that require robust security in their file transfer processes. Its support for various encryption protocols and integrated clustering makes it suitable for enterprises dealing with sensitive data and needing compliance with stringent security standards.
Pros:
- Supports multiple file transfer protocols including SFTP, FTPS, HTTPS, and AS2.
- Drummond Certified for AS2, ensuring compliance and reliability in file transfers.
- Features integrated clustering support for better performance and scalability.
- Includes a comprehensive Key and Certificate Management System (KMS) for efficient encryption management.
Cons:
- The extensive range of features and security protocols may present a steep learning curve for some users.
- Might be more complex and feature-rich than required for smaller organizations with simpler file transfer needs.
Conclusion
AS2’s end-to-end encryption, along with its use of digital certificates, are valid reasons why AS2 is becoming popular and sometimes even required. Additionally, AS2 also provides the non-repudiation functionalities to validate the file integrity with transfer receipts— something not familiar with standard file transfer protocols.
If your organization is in the retail or e-commerce industry, then AS2 is probably a good idea. This protocol will help you meet the compliance and the requirements of many trading partners. Still, the AS2 protocol is not easy to implement and requires special software; this is why most businesses use safe file transfer mechanisms like SFTP. This protocol is easier to implement and provides strong authentication (including keys and passwords).
AS2 Protocol FAQs
What is the AS2 protocol?
The AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) protocol is a secure and reliable data exchange protocol that is commonly used for exchanging electronic data between businesses over the Internet. It is a standard for secure, reliable, and efficient data exchange, and is widely used for exchanging electronic invoices, purchase orders, and other business-to-business (B2B) transactions.
Why use the AS2 protocol?
The AS2 protocol is used because it provides a secure and reliable method for exchanging electronic data between businesses. The protocol includes features such as data encryption, digital signatures, and message authentication, ensuring that data is protected from tampering and unauthorized access. Additionally, the AS2 protocol provides for guaranteed delivery of messages, ensuring that data is exchanged accurately and efficiently.
What are the key features of the AS2 protocol?
The key features of the AS2 protocol include:
- Data encryption: The ability to encrypt data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Digital signatures: The ability to use digital signatures to authenticate the identity of the sender and the integrity of the data being exchanged.
- Message authentication: The ability to verify the authenticity of messages to prevent tampering and ensure the reliability of the data being exchanged.
- Guaranteed delivery: The ability to ensure that messages are delivered accurately and efficiently, with delivery receipts and error reporting.
- What are the benefits of using the AS2 protocol?
- The benefits of using the AS2 protocol include:
- Improved security: The AS2 protocol provides a secure method for exchanging electronic data, protecting it from unauthorized access and tampering.
- Improved reliability: The AS2 protocol provides for guaranteed delivery of messages, ensuring that data is exchanged accurately and efficiently.
- Improved efficiency: The AS2 protocol provides for automated data exchange, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors.
- Improved compliance: The AS2 protocol is widely adopted and is a recognized standard for secure and reliable data exchange, helping organizations meet compliance requirements.